了解冒泡排序算法:分步指南
来源:dev.to
时间:2024-12-31 10:30:58 344浏览 收藏
亲爱的编程学习爱好者,如果你点开了这篇文章,说明你对《了解冒泡排序算法:分步指南》很感兴趣。本篇文章就来给大家详细解析一下,主要介绍一下,希望所有认真读完的童鞋们,都有实质性的提高。
图片来源:medium
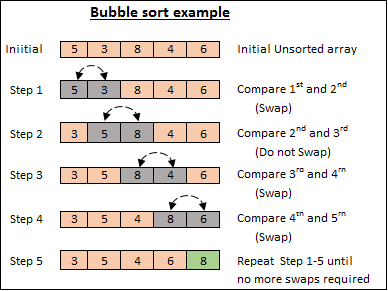
排序是数据结构和算法中最重要的部分之一。排序算法有很多种,这是最简单的算法之一:冒泡排序。
排序算法是计算机科学的基础,而冒泡排序是最简单、最直观的排序算法之一。这篇文章将探讨冒泡排序的工作原理,分析其时间复杂度,并演练 javascript 实现。
在本系列中,我将分享使用 javascript 的完整排序算法数据结构和算法,并从冒泡排序开始。如果您喜欢并希望我通过示例分享完整的排序算法,请喜欢并关注我。它激励我为你们创建和准备内容。
什么是冒泡排序?
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,它重复遍历列表,比较相邻元素(下一个元素),如果顺序错误则交换它们。重复此过程直到列表排序完成。该算法因其较小的元素“冒泡”到列表顶部而得名。
javascript 实现:
让我们深入代码看看冒泡排序是如何在 javascript 中实现的:
// by default ascending order
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of an array
//the outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//if the length is n then the outer loop runs n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//if the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
for (let j = 0; j > len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if the first element greater than to the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array; // return the sorted array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
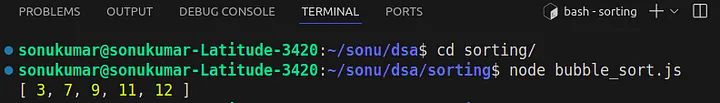
输出
按降序排序:
// descending order
function bubble_sort_descending_order(array) {
const len = array.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
// checking if first element greter than next element,
if (array[j] < array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort_descending_order(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [ 12, 11, 9, 7, 3 ]
输出:

已经添加了注释并解释了上面的每一行代码。但我也会详细解释,以帮助您理解完整的流程和代码。
工作原理:
- 初始化:我们首先确定数组的长度,这有助于控制迭代次数。
- 外循环:该循环运行 n-1 次,其中 n 是数组的长度。每次迭代都会确保下一个最大元素被放置在正确的位置。
- 内循环:对于外循环的每一次循环,内循环都会比较相邻元素,如果它们无序,则交换它们。内部循环的范围随着每次传递而减小,因为最大的元素已经排序在数组的末尾。
- 交换:如果一个元素大于下一个元素,则使用临时变量交换它们。
- 返回:最后返回排序后的数组。
优化版本:
// optimized version:
function bubble_sort(array) {
const len = array.length; // get the length of the array
//the outer loop controls the inner loop, which means the outer loop will decide how many times the inner loop will be run.
//if the length is n then the outer loop run n-1 times.
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
// inner loop will run based on the outer loop and compare the value,
//if the first value is higher than the next value then swap it, loop must go on for each lowest value
let isswapped = false;
for (let j = 0; j < len - i -1; j++) {
//check if the first element is greater than the next element
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// then, swap the value array[j] to array[j+1]
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isswapped = true;
}
}
//if no element swap by inner loop then break;
if (isswapped === false) {
break;
}
}
return array;
}
const array = [7, 12, 9, 11, 3]; // input data
console.log(bubble_sort(array));
// output data after sorted!
// [3, 7, 9, 11, 12];
说明:
- for (令 i = 0; i < len — 1; i ) 这是外部循环,运行 n-1 次,其中 n 是数组的长度。外循环控制内循环执行的次数。外循环的每次迭代都会确保下一个最大元素被放置在正确的位置。
- 让 isswapped = false 布尔变量 isswapped 被初始化为 false。该变量用于跟踪在内部循环的当前传递期间是否交换了任何元素。如果没有发生交换,则数组已经排序,算法可以提前终止。
- for (让 j = 0; j < len — i — 1; j ) { 这是内部循环,它迭代数组元素直到 len - i - 1。 - i 部分确保循环不考虑在之前的循环中已经排序的元素。
- if (数组[j] > 数组[j 1]) { 此条件检查当前元素是否大于下一个元素。如果为 true,则需要进行交换才能正确排序元素。
let temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
isswapped = true;
- 这些行使用临时变量 temp 执行元素 array[j] 和 array[j 1] 的交换。交换后,isswapped 设置为 true,表示发生了交换。
if (isSwapped === false) {
break;
}
- 内部循环完成后,此条件检查 isswapped 是否仍然为 false。如果没有进行交换,则数组已经排序,并且可以使用break提前退出外循环。
- 最后返回排序后的数组。
时间复杂度
在最坏和平均情况下,冒泡排序的时间复杂度为 (o(n²)),其中 (n) 是数组中元素的数量。这是因为每个元素都会与其他元素进行比较。在最好的情况下,当数组已经排序时,如果添加优化以在不需要交换时停止算法,时间复杂度可以是 (o(n))。
在最好的情况下,当数组已经排序时,由于 isswapped 优化,算法可以提前终止,导致时间复杂度为 (o(n))。
总体而言,由于其二次时间复杂度,冒泡排序对于大型数据集效率不高,但对于小型数组或作为理解排序算法的教育工具可能很有用。
结论
冒泡排序由于其简单性而成为一种用于教育目的的优秀算法。然而,由于其二次时间复杂度,它不适合大型数据集。尽管冒泡排序效率低下,但理解冒泡排序为学习更高级的排序算法奠定了基础。
文中关于的知识介绍,希望对你的学习有所帮助!若是受益匪浅,那就动动鼠标收藏这篇《了解冒泡排序算法:分步指南》文章吧,也可关注golang学习网公众号了解相关技术文章。
-
502 收藏
-
501 收藏
-
501 收藏
-
501 收藏
-
501 收藏
-
302 收藏
-
127 收藏
-
131 收藏
-
235 收藏
-
185 收藏
-
142 收藏
-
483 收藏
-
481 收藏
-
477 收藏
-
294 收藏
-
445 收藏
-
407 收藏
-

- 前端进阶之JavaScript设计模式
- 设计模式是开发人员在软件开发过程中面临一般问题时的解决方案,代表了最佳的实践。本课程的主打内容包括JS常见设计模式以及具体应用场景,打造一站式知识长龙服务,适合有JS基础的同学学习。
- 立即学习 543次学习
-

- GO语言核心编程课程
- 本课程采用真实案例,全面具体可落地,从理论到实践,一步一步将GO核心编程技术、编程思想、底层实现融会贯通,使学习者贴近时代脉搏,做IT互联网时代的弄潮儿。
- 立即学习 516次学习
-

- 简单聊聊mysql8与网络通信
- 如有问题加微信:Le-studyg;在课程中,我们将首先介绍MySQL8的新特性,包括性能优化、安全增强、新数据类型等,帮助学生快速熟悉MySQL8的最新功能。接着,我们将深入解析MySQL的网络通信机制,包括协议、连接管理、数据传输等,让
- 立即学习 500次学习
-

- JavaScript正则表达式基础与实战
- 在任何一门编程语言中,正则表达式,都是一项重要的知识,它提供了高效的字符串匹配与捕获机制,可以极大的简化程序设计。
- 立即学习 487次学习
-

- 从零制作响应式网站—Grid布局
- 本系列教程将展示从零制作一个假想的网络科技公司官网,分为导航,轮播,关于我们,成功案例,服务流程,团队介绍,数据部分,公司动态,底部信息等内容区块。网站整体采用CSSGrid布局,支持响应式,有流畅过渡和展现动画。
- 立即学习 485次学习

